- basis
- (
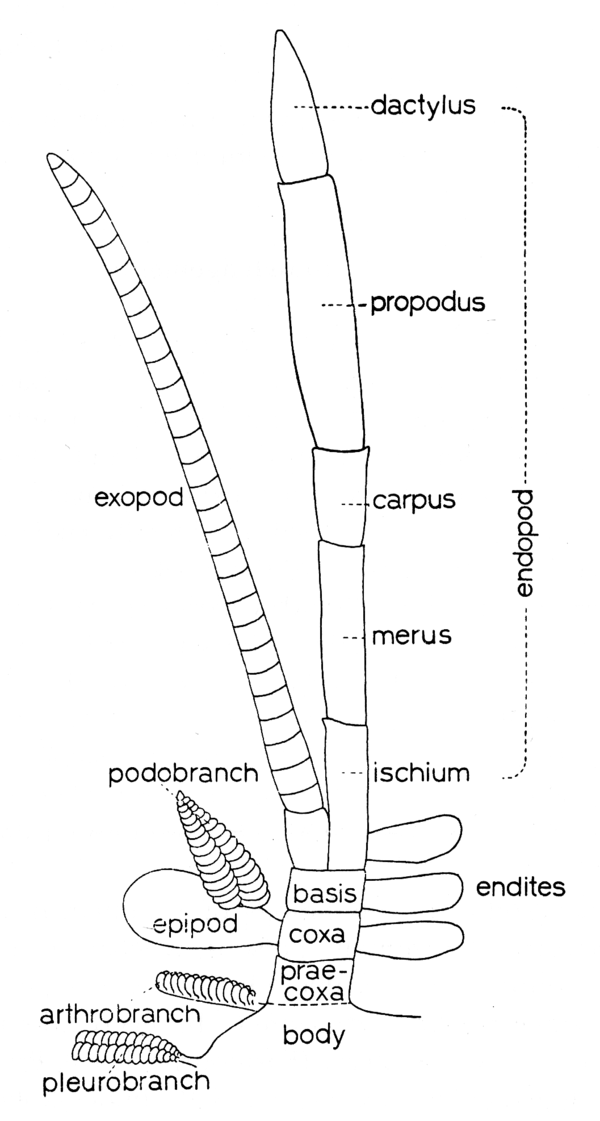 ) [Holthuis, 1993].Schematic drawing of a thoracic leg. [Holthuis, 1993]Article 2 of thoracic and abdominal appendages [Holdich and Jones, 1983].Limb segments adjoining coxa on its distal side and commonly bearing endopod and exopod; in nonpedunculate cirripeds comprises basal calcareous or membranous plate which furnishes anchorage to foreign body or substrate. (Syn. basipod(ite)) [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Second article (from body) of leg or maxilliped. Sixth segment from distal end of limb. (Syn. basipodite) [Williams, 1984].Second article of limb. (Pl. bases) [Poore, 2004].Second podomere or segment, from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage (Fig. 3C). (Pl. bases) [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997].Second segment (from proximal end) of segmented appendage [Hobbs and Jass, 1988].Second segment from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage. (Pl. bases) [Butler, T.H.].Second segment of a pereiopod or maxilliped counted from the proximal end, immovably united with the ischium [Ingle, 1983].Segment of protopod adjoining coxa and carrying exopod and endopod distally; also basal calcareous or membranous plate furnishing anchorage to substrate in sessile cirripeds. (Pl. bases) [McLaughlin, 1980].The second segment from the proximal end of a segmented appendage [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].The second segment from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage. (Pl. bases) [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The second segment of a thoracic limb. See: pereopod [Wilson, 1989].(Order Cladocera):Second segment of appendage; from distal segment of protopod (coax, basis). Often fused and indistinguishable. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Cephalocarida):Protopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Elongate second segment of thoracopod (maxillipeds and pereopods) or pleopods. May bear five-segmented endopod and smaller exopod. (See also epipod) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Second of seven segments (coxa, basis, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopod. Bears endite in maxillae and maxillipeds. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Second segment of appendage (thoracopod); forms distal segment of protopod (coxa, basis) and bears variously developed branches (endopod, exopod). May be fused to following segment (ischium) to form ischiobasis. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Amphipoda):Second of seven segments of thoracopod (coxa, basis, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus); represents first movable (free) segment. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):(
) [Holthuis, 1993].Schematic drawing of a thoracic leg. [Holthuis, 1993]Article 2 of thoracic and abdominal appendages [Holdich and Jones, 1983].Limb segments adjoining coxa on its distal side and commonly bearing endopod and exopod; in nonpedunculate cirripeds comprises basal calcareous or membranous plate which furnishes anchorage to foreign body or substrate. (Syn. basipod(ite)) [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Second article (from body) of leg or maxilliped. Sixth segment from distal end of limb. (Syn. basipodite) [Williams, 1984].Second article of limb. (Pl. bases) [Poore, 2004].Second podomere or segment, from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage (Fig. 3C). (Pl. bases) [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997].Second segment (from proximal end) of segmented appendage [Hobbs and Jass, 1988].Second segment from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage. (Pl. bases) [Butler, T.H.].Second segment of a pereiopod or maxilliped counted from the proximal end, immovably united with the ischium [Ingle, 1983].Segment of protopod adjoining coxa and carrying exopod and endopod distally; also basal calcareous or membranous plate furnishing anchorage to substrate in sessile cirripeds. (Pl. bases) [McLaughlin, 1980].The second segment from the proximal end of a segmented appendage [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].The second segment from the proximal end of a typically 7-segmented appendage. (Pl. bases) [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The second segment of a thoracic limb. See: pereopod [Wilson, 1989].(Order Cladocera):Second segment of appendage; from distal segment of protopod (coax, basis). Often fused and indistinguishable. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Cephalocarida):Protopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Elongate second segment of thoracopod (maxillipeds and pereopods) or pleopods. May bear five-segmented endopod and smaller exopod. (See also epipod) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Second of seven segments (coxa, basis, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopod. Bears endite in maxillae and maxillipeds. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Second segment of appendage (thoracopod); forms distal segment of protopod (coxa, basis) and bears variously developed branches (endopod, exopod). May be fused to following segment (ischium) to form ischiobasis. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Amphipoda):Second of seven segments of thoracopod (coxa, basis, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus); represents first movable (free) segment. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):(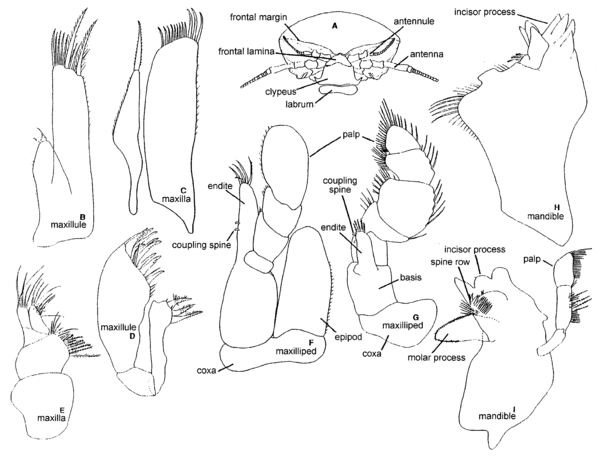 ) [Wetzer et al. 1997].Nomenclature of isopod cephalon (A). Examples of isopod mouth appendages: Idoteidae (B, C, F, H); Cirolanidae (D, E, G, I). [Wetzer et al. 1997](Order Isopoda):Article of appendage adjoining coxa proximally, and carrying endopod distally, i.e., article 2 of pereopod [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].(
) [Wetzer et al. 1997].Nomenclature of isopod cephalon (A). Examples of isopod mouth appendages: Idoteidae (B, C, F, H); Cirolanidae (D, E, G, I). [Wetzer et al. 1997](Order Isopoda):Article of appendage adjoining coxa proximally, and carrying endopod distally, i.e., article 2 of pereopod [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].(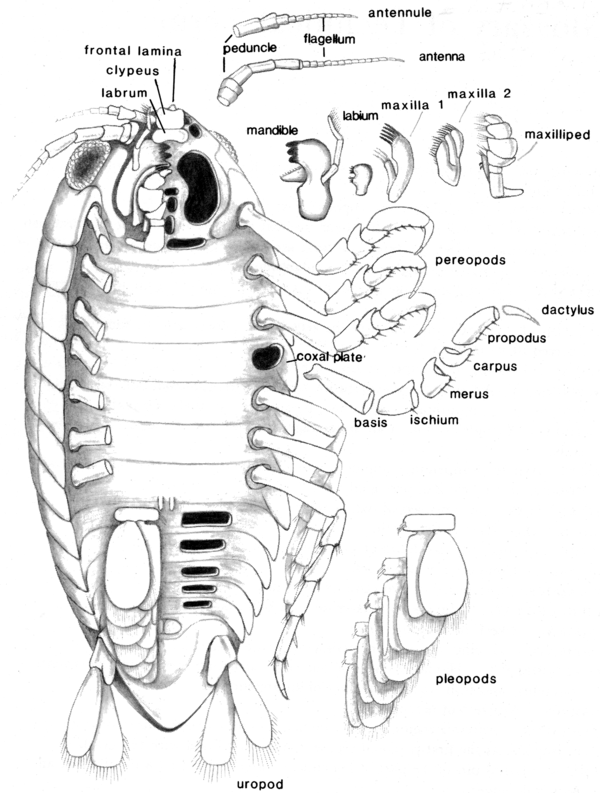 ) [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].Schematic representation of an isopod illustrating morphological terms. [Kensley and Schotte, 1989](Order Isopoda):Second segment of pereopod; located between coxa and ischium. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Mysida):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Third segment of thoracic appendage (thoracopod); located between coxa and merus. Also interpreted as being second segment (between coxa and ischium). (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):In thoracopod, third of three segments (precoxa, coax, basis) of protopod; may also be applied to segment of antennule. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):Basal element by which unstalked barnacle is attached to substratum. (calcareous = solid, membranous) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):Second segment of appendage; forms distal segment of protopod (coxa, basis). (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):The distal segment of the protopod of postantennulary appendages, bearing the rami [Boxshall and Halsey, 2004].(Subclass Copepoda):The distal segment of the protopod; it bears no more than two ventral, setose endites. The rami, exopod and endopod of a limb, originate on the basis (see coxa and praecoxa) [Ferrari and Dahms, in press].(Subclass Mystacocarida):Protopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):Distal part of divided protopod (separated from coxa by suture) [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Superorder Syncarida):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. Frequently interpreted as being fused with following segment (ischium) in maxilliped endopod. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):
) [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].Schematic representation of an isopod illustrating morphological terms. [Kensley and Schotte, 1989](Order Isopoda):Second segment of pereopod; located between coxa and ischium. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Mysida):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Third segment of thoracic appendage (thoracopod); located between coxa and merus. Also interpreted as being second segment (between coxa and ischium). (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):In thoracopod, third of three segments (precoxa, coax, basis) of protopod; may also be applied to segment of antennule. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):Basal element by which unstalked barnacle is attached to substratum. (calcareous = solid, membranous) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):Second segment of appendage; forms distal segment of protopod (coxa, basis). (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):The distal segment of the protopod of postantennulary appendages, bearing the rami [Boxshall and Halsey, 2004].(Subclass Copepoda):The distal segment of the protopod; it bears no more than two ventral, setose endites. The rami, exopod and endopod of a limb, originate on the basis (see coxa and praecoxa) [Ferrari and Dahms, in press].(Subclass Mystacocarida):Protopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):Distal part of divided protopod (separated from coxa by suture) [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Superorder Syncarida):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Second of two segments (coxa, basis) of proximal part (protopod) of appendage. Frequently interpreted as being fused with following segment (ischium) in maxilliped endopod. (Syn. basipodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):
Crustacea glossary. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. 2011.
