- endopod
- (
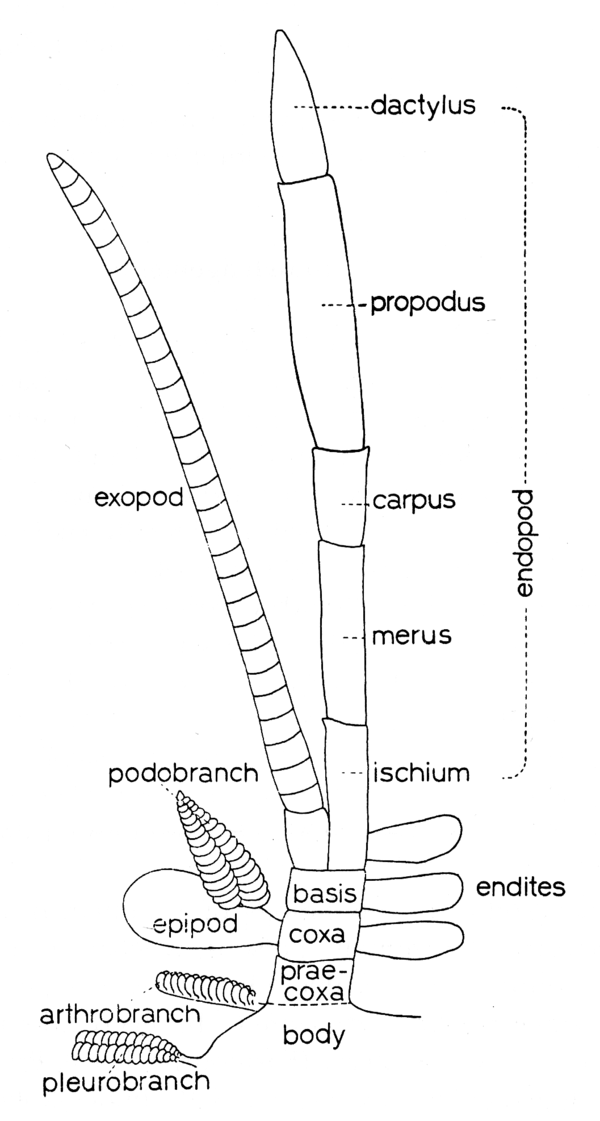 ) [Holthuis, 1993].Schematic drawing of a thoracic leg. [Holthuis, 1993]Inner branch of biramous appendage, especially one arising from protopodite of pleopod [Butler, T.H.].Inner of two branches of biramous limb, comprising ischium through to dactylus; in many the dominant or only branch. (Syn. endopodite) [Poore, 2004].Inner ramus of biramous appendage [McLaughlin, 1980].Innermost ramus of limb arising from protopod basis; in the Eumalacostraca typically composed of five segments (ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Medial of two rami arising from the protopod and constituting the biramous limb [Brusca and Brusca, 2002].Mesial ramus of a biramus appendage, especially one arising from the basis or from the protopodite of the pleopod [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997].Mesial ramus of biramus appendage, originating on basal segment (basis) (see Fig. 13) [Hobbs and Jass, 1988].The inner branch of a biramous appendage [Ingle, 1983].The inner of the two branches of the primitive appendage (Fig. 2) [Warner, 1977].The medial or interior ramus of a crustacean appendage. In the Isopoda, another name for a thoracic appendage (exclusive of the coxa and basis), although more typically applied to the inner ramus of a pleopod or a uropod [Wilson, 1989].The mesial branch of a bifurcate appendage, especially one arising from the protopodite of the pleopod of shrimps [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The mesial ramus if a biramus appendage, having its origin on the basis [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].(Order Cladocera):Lobe-like inner branch (ramus) of trunk appendage; lacks articulation with protopodal part of appendage and is more or less continuous with distal endites. Forms entire distal part of limb in certain predatory water fleas. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Notostraca):Inner lobe at distal end of thoracopod or abdominal appendage in certain tadpole shrimp. Most distal (sixth) endite also occasionally termed endopod. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Diplostraca):Unsegmented, lobe-like inner branch of trunk appendage; often termed sixth endite. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Anostraca):Inner branch of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). Unsegmented, lobe-like, and bearing marginal setae. Not articulated with protopod and therefore occasionally termed sixth endite. Serves in feeding. (oval, rectangular) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Cephalocarida):Inner branch of biramous appendage. Refers to twosegmented branch of antennae, lobate branch (in larvae only) of mandibles, annulate branch of maxillules, six-segmented branch of maxillae, and five to six-segmented branch of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Forms palp of maxillule and represents main five-segmented branch of thoracopod (maxillipeds and pereopods). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Inner branch (ramus) of binamous appendage. Represents only branch or main, typically five-segmented branch (ischium, mercus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopod. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to threesegmented part of peduncle of antenna, palp-shaped or more elongate inner branch of mouthparts, inner branch of pleopods and uropods; considered to represent main, basically five-segmented part of pereopod. (paddle-shaped, palp-shaped, pediform). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Amphipoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Forms palp in mouthparts (mandibles, maxillules, maxillae, maxillipeds) and represents main five-segmented part of pereopods. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):Inner (medial) ramus of an appendage [Wetzer et al. 1997].(Order Isopoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):Inner ramus of a biramous appendage [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].(Order Mysida):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents palp of maxillae and maxillules as well as inner branch of maxillipeds, pereopods, and pleopods. Endopod of uropod may bear statocyst. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to threesegmented, flagellum-bearing branch of antennae, appendix interna-bearing branch of pleopods, and one-segmented branch of uropods, while it is considered to represent outer branch of last three thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Leptostraca):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. (simple, two-, three- to four-, five-segmented) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):Setose inner branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). (See also exopod) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):(
) [Holthuis, 1993].Schematic drawing of a thoracic leg. [Holthuis, 1993]Inner branch of biramous appendage, especially one arising from protopodite of pleopod [Butler, T.H.].Inner of two branches of biramous limb, comprising ischium through to dactylus; in many the dominant or only branch. (Syn. endopodite) [Poore, 2004].Inner ramus of biramous appendage [McLaughlin, 1980].Innermost ramus of limb arising from protopod basis; in the Eumalacostraca typically composed of five segments (ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) [Moore and McCormick, 1969].Medial of two rami arising from the protopod and constituting the biramous limb [Brusca and Brusca, 2002].Mesial ramus of a biramus appendage, especially one arising from the basis or from the protopodite of the pleopod [Perez Farfante and Kensley, 1997].Mesial ramus of biramus appendage, originating on basal segment (basis) (see Fig. 13) [Hobbs and Jass, 1988].The inner branch of a biramous appendage [Ingle, 1983].The inner of the two branches of the primitive appendage (Fig. 2) [Warner, 1977].The medial or interior ramus of a crustacean appendage. In the Isopoda, another name for a thoracic appendage (exclusive of the coxa and basis), although more typically applied to the inner ramus of a pleopod or a uropod [Wilson, 1989].The mesial branch of a bifurcate appendage, especially one arising from the protopodite of the pleopod of shrimps [Chace and Hobbs, 1969].The mesial ramus if a biramus appendage, having its origin on the basis [Hobbs, Hobbs, and Daniel 1977].(Order Cladocera):Lobe-like inner branch (ramus) of trunk appendage; lacks articulation with protopodal part of appendage and is more or less continuous with distal endites. Forms entire distal part of limb in certain predatory water fleas. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Notostraca):Inner lobe at distal end of thoracopod or abdominal appendage in certain tadpole shrimp. Most distal (sixth) endite also occasionally termed endopod. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Diplostraca):Unsegmented, lobe-like inner branch of trunk appendage; often termed sixth endite. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Anostraca):Inner branch of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). Unsegmented, lobe-like, and bearing marginal setae. Not articulated with protopod and therefore occasionally termed sixth endite. Serves in feeding. (oval, rectangular) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Cephalocarida):Inner branch of biramous appendage. Refers to twosegmented branch of antennae, lobate branch (in larvae only) of mandibles, annulate branch of maxillules, six-segmented branch of maxillae, and five to six-segmented branch of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Cumacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Forms palp of maxillule and represents main five-segmented branch of thoracopod (maxillipeds and pereopods). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Tanaidacea):Inner branch (ramus) of binamous appendage. Represents only branch or main, typically five-segmented branch (ischium, mercus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopod. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Decapoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to threesegmented part of peduncle of antenna, palp-shaped or more elongate inner branch of mouthparts, inner branch of pleopods and uropods; considered to represent main, basically five-segmented part of pereopod. (paddle-shaped, palp-shaped, pediform). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Amphipoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Forms palp in mouthparts (mandibles, maxillules, maxillae, maxillipeds) and represents main five-segmented part of pereopods. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):Inner (medial) ramus of an appendage [Wetzer et al. 1997].(Order Isopoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Isopoda):Inner ramus of a biramous appendage [Kensley and Schotte, 1989].(Order Mysida):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents palp of maxillae and maxillules as well as inner branch of maxillipeds, pereopods, and pleopods. Endopod of uropod may bear statocyst. (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Stomatopoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to threesegmented, flagellum-bearing branch of antennae, appendix interna-bearing branch of pleopods, and one-segmented branch of uropods, while it is considered to represent outer branch of last three thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Leptostraca):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. (simple, two-, three- to four-, five-segmented) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Branchiura):Setose inner branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod). (See also exopod) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Cirripedia):(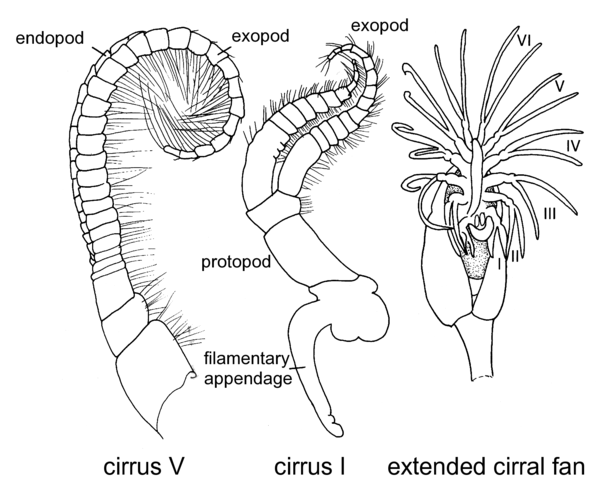 ) [Anderson, 1980].Lepas anatifera: cirrus V; cirrus I, and extended cirral fan. [Anderson, 1980](Subclass Cirripedia):Inner branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod in ascothoracican, cirrus in other cirripeds). (one- to three-jointed, multiarticulate) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):A ventral extension of the proximodistal axis of a limb originating on the basis of the protopod and usually segmented. Dorsal setae are absent from endopodal segments except for the penultimate and the antepenultimate segments. An endopodal segment may bear more than one ventral seta [Ferrari and Dahms, in press].(Subclass Copepoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to inner, main, or only branch of antenna and maxilliped, as well as to inner branch of mandible, maxillule, and pereopod. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):The inner ramus of a biramous appendage [Boxshall and Halsey, 2004].(Subclass Mystacocarida):Inner branch of biramous appendage. Refers to four- segmented branch of antenna and mandible of three-segmented branch of maxilliped. Single branch of uniramous appendage (e.g., maxilla) may also be interpreted as representing and endopod. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):In distally biramous crustacean limb, the medial ramus. (Syn. endopodite) [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Class Ostracoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Typically forms palp-like structure in mouthparts (e.g., mandible, maxillules) or main component of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Remipedia):Inner or more ventral branch (ramus) of biramous appendage (antennule, antenna, trunk limb). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Superorder Syncarida):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Basically sixsegmented in throracopods, consisting of preischium, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus and dactylus. (See also exopod, gonophysis). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents only branch (flagellum) of antenna, palp of anterior mouthparts, and larger, basically fivesegmented ramus (ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents flagellum-bearing branch of antenna, palp-like branch of maxillules and maxillae, five-segmented main branch of thoracopods, and flattened inner branch of pleopods and uropods. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].
) [Anderson, 1980].Lepas anatifera: cirrus V; cirrus I, and extended cirral fan. [Anderson, 1980](Subclass Cirripedia):Inner branch (ramus) of thoracic appendage (thoracopod in ascothoracican, cirrus in other cirripeds). (one- to three-jointed, multiarticulate) (see also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):A ventral extension of the proximodistal axis of a limb originating on the basis of the protopod and usually segmented. Dorsal setae are absent from endopodal segments except for the penultimate and the antepenultimate segments. An endopodal segment may bear more than one ventral seta [Ferrari and Dahms, in press].(Subclass Copepoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Refers to inner, main, or only branch of antenna and maxilliped, as well as to inner branch of mandible, maxillule, and pereopod. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Subclass Copepoda):The inner ramus of a biramous appendage [Boxshall and Halsey, 2004].(Subclass Mystacocarida):Inner branch of biramous appendage. Refers to four- segmented branch of antenna and mandible of three-segmented branch of maxilliped. Single branch of uniramous appendage (e.g., maxilla) may also be interpreted as representing and endopod. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Ostracoda):In distally biramous crustacean limb, the medial ramus. (Syn. endopodite) [Cohen, Peterson, and Maddocks, in press].(Class Ostracoda):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Typically forms palp-like structure in mouthparts (e.g., mandible, maxillules) or main component of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Class Remipedia):Inner or more ventral branch (ramus) of biramous appendage (antennule, antenna, trunk limb). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Superorder Syncarida):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Basically sixsegmented in throracopods, consisting of preischium, ischium, merus, carpus, propodus and dactylus. (See also exopod, gonophysis). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Thermosbaenacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents only branch (flagellum) of antenna, palp of anterior mouthparts, and larger, basically fivesegmented ramus (ischium, merus, carpus, propodus, dactylus) of thoracopods. (See also exopod). (Syn. endopodite) [Stachowitsch, 1992].(Order Euphausiacea):Inner branch (ramus) of biramous appendage. Represents flagellum-bearing branch of antenna, palp-like branch of maxillules and maxillae, five-segmented main branch of thoracopods, and flattened inner branch of pleopods and uropods. (Syn. endopodite) See: exopod [Stachowitsch, 1992].
Crustacea glossary. Natural History Museum of Los Angeles County. 2011.
